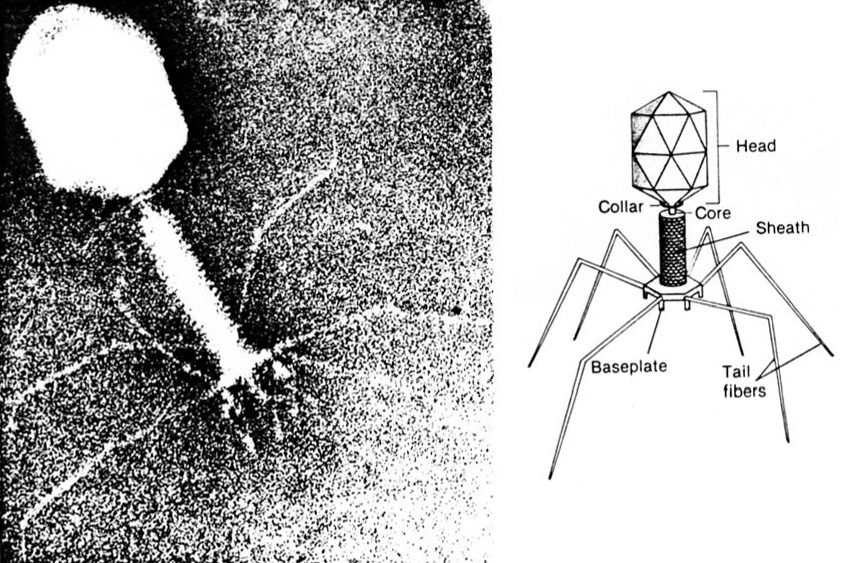
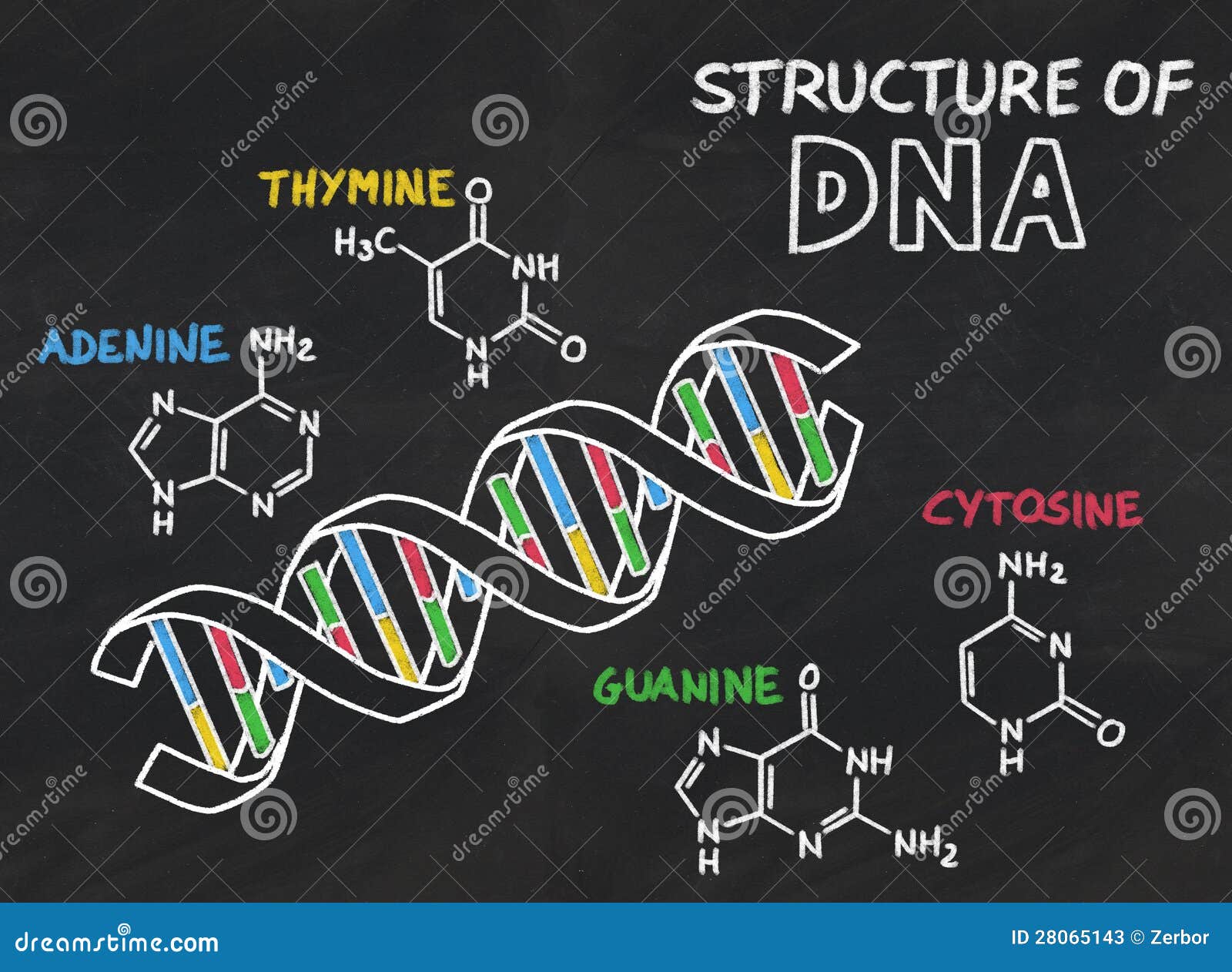
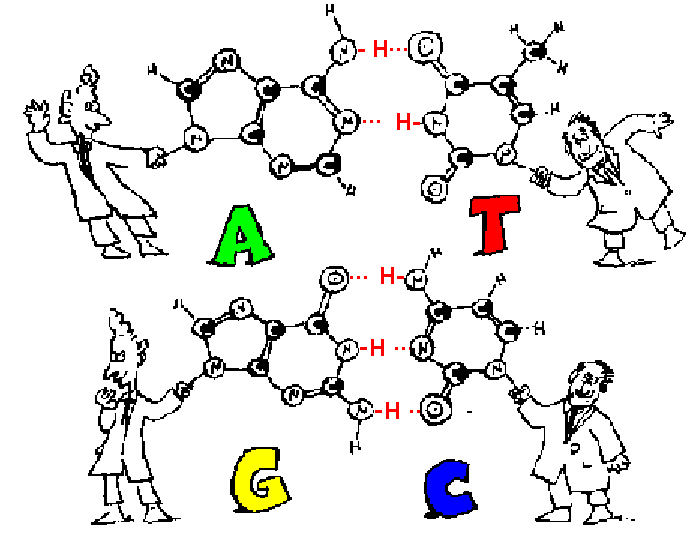
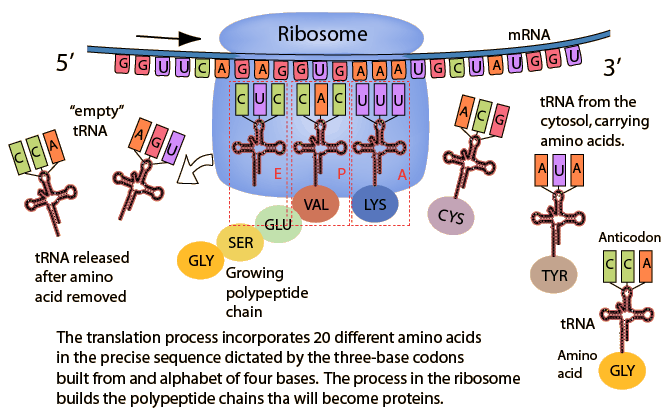
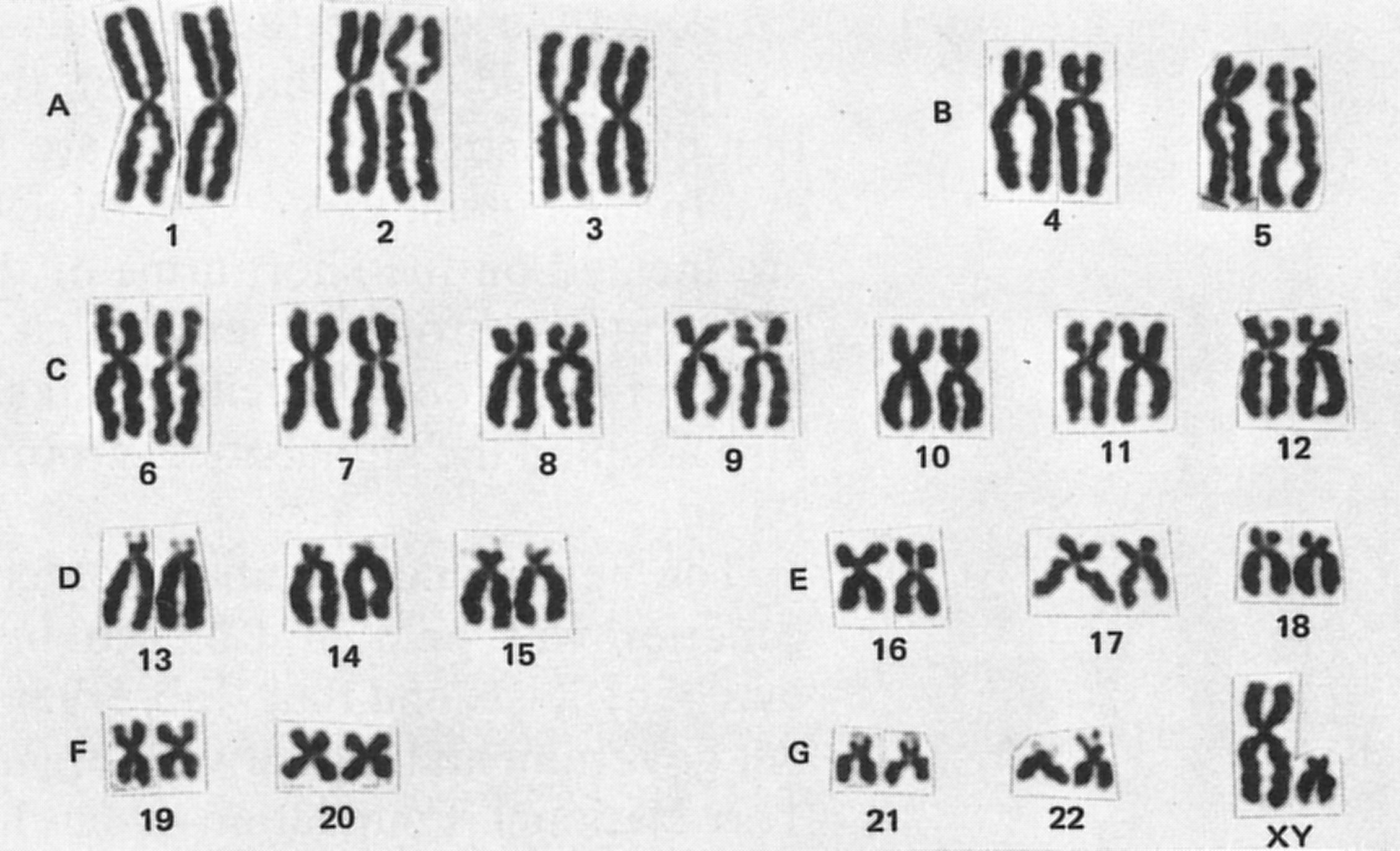
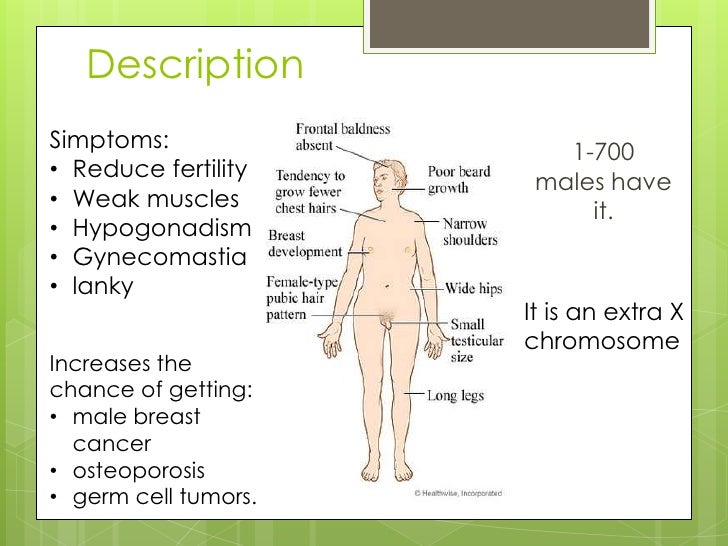
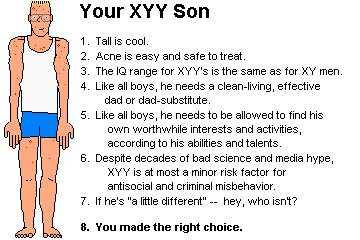
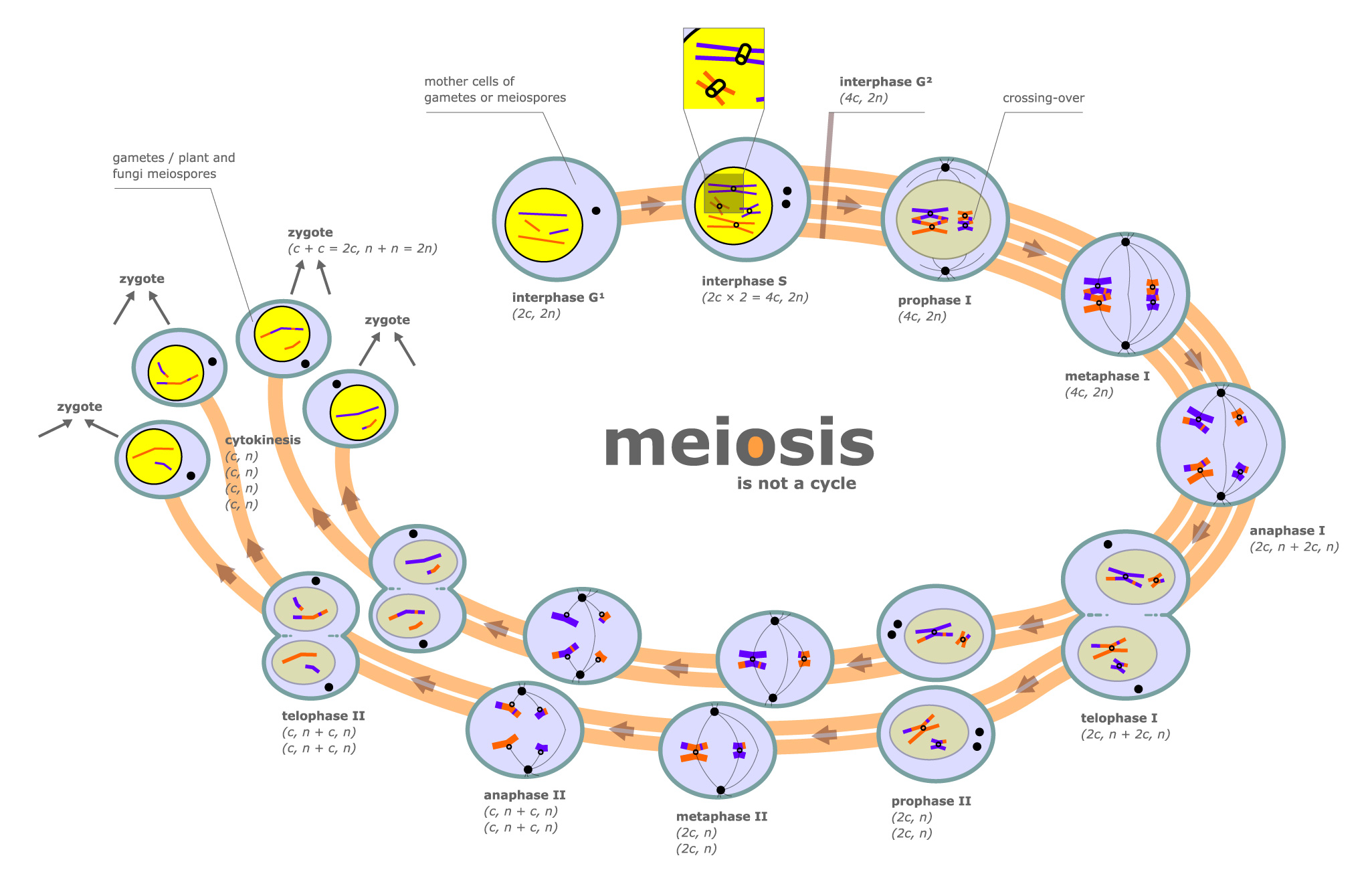
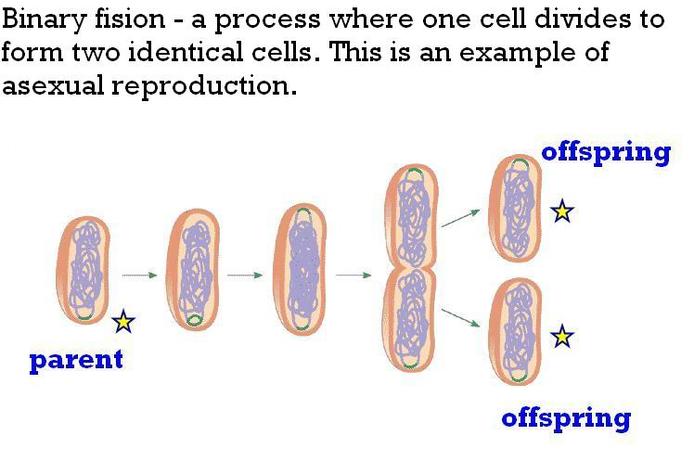
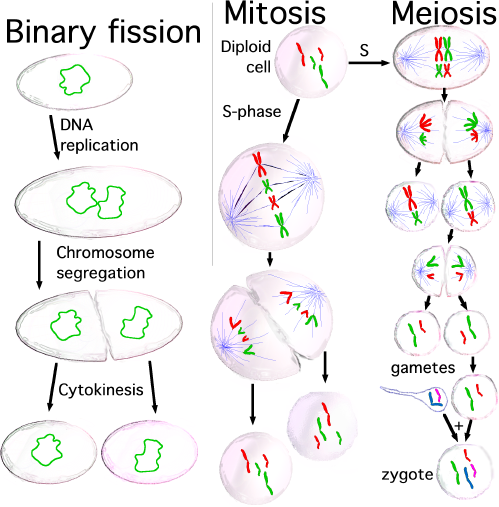PBL for DECEMBER -DNA Extraction Kit
- References: Only use Websites ending in .gov, .edu , .net , .org. references ending in .com will not be allowed for your research.
- DO NOT USE wikipedia.org, this is the only .org website you are not allowed to use.
- Minimum 6 references.
PBL LAUNCHThis assignment will be due on December 15, 2015