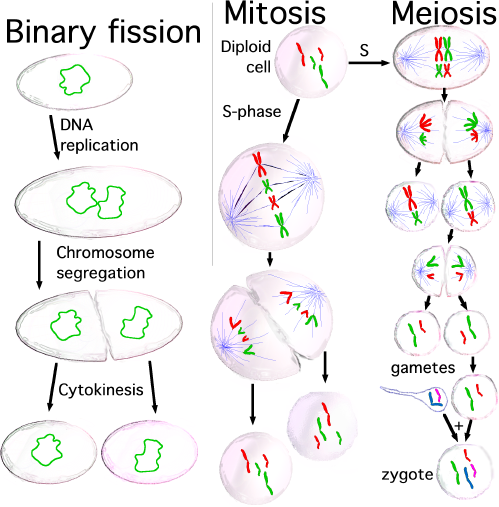Section 5.3 Regulation of Cell Cycle
The regulation, or control, of the cell cycle is important for healthy cells to grow. Having uncontrollable division results in what we know as CANCER!
Take a look at this video....
Cancer Cells vs Normal Cells
The cell uses Internal and External Factors
External Factors: The cell uses physical and chemical signals to control the cell cycle. When cells get around other cells they stop dividing.
Many cells release chemicals to neighboring cells to begin to divide.
Internal Factors: When external factors bind to cells they cause a response inside the cell. Enzymes and proteins help the cell move through the cell cycle.
Apoptosis: Programmed cell death. When the cell is damaged or it is no longer useful it programs itself to die. This avoids any problem the cell might contain from spreading to neighboring cells.
take a look...
Apoptosis
Uncontrolled Cell Division
Benign tumors: relatively harmless because they clump together and can be removed
Malignant tumors: cancer cells that break away from the tumor and travel to other parts of the body.
Metastasize: Once the malignant tumors break away and travel through the blood stream they appear at other parts of the body
Metastasis
Carcinogens substances that are known to cause or lead to cancer
Is Red Meat Giving You Cancer
Benign Tumor?
Lets review
Section 5.4 Asexual Reproduction
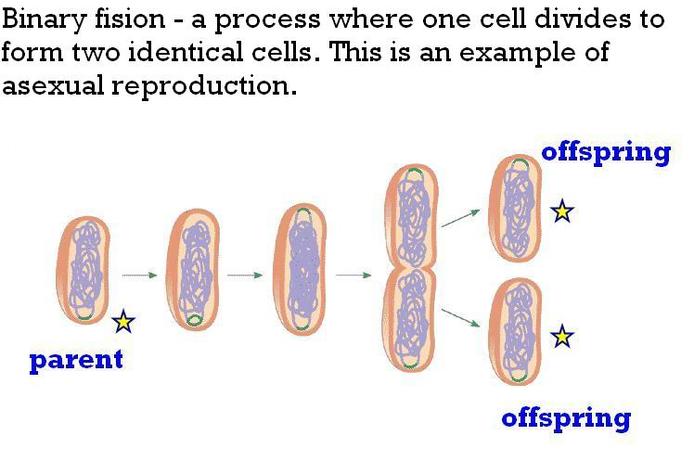
Asexual reproduction is the production of offspring from a single parent. The offspring are, for the most part, genetically identical to each other and to the parent.
Usually seen in prokaryotes. Eukaryotes undergo asexual reproduction through mitosis.
- Multicellular organisms undergo a different type of asexual reproduction called known as mitosis, vegetative reproduction, and/or "budding". EX: Starfish, Hydra
Budding/Fission in Starfish
Parthenogenics
Eukaryote Binary Fission
Prokaryote Binary Fission
Advantage & Disadvantage of
asexual reproduction
Why Sex?
Advantage & Disadvantage of asexual reproduction
Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
Section 5: Multicellular Life
Level of organization
Cell differentiation: the process by which cells that do not have a specialized function develop a specialized function.
What Are Stem Cells?
How Do They Get Stem Cells?
Growing Organs From Stem Cells
A Stem Cell Story
Trachea Transplant Using Stem Cells