1.2 UNIFYING THEMES OF BIOLOGY
HOW ARE THINGS SORTED?
ITEMS ARE ORGANIZED FROM SMALLEST TO BIGGEST.
Living things share 4 common characteristics
1. CELLS: ALL ORGANISMS ARE MADE UP OF CELLS
2. NEED FOR ENERGY: ALL ORGANISMS NEED CHEMICAL ENERGY TO CARRY OUT THEIR FUNCTIONS
3. RESPOND TO ENVIRONMENT—ALL ORGANISMS MUST RESPOND TO STIMULI TO SURVIVE.
4. REPRODUCTION—ORGANISMS MUST HAVE THE ABILITY TO REPRODUCE IN ORDER FOR A SPECIES TO SURVIVE.
WHAT DO ALL THESE PICTURES HAVE IN COMMON?


Systems—Related parts interact to form a whole.
What function do these structures have on these organisms?
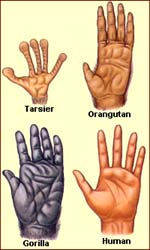



Structure and Function— Function is related to structure.
Think Turn Talk......
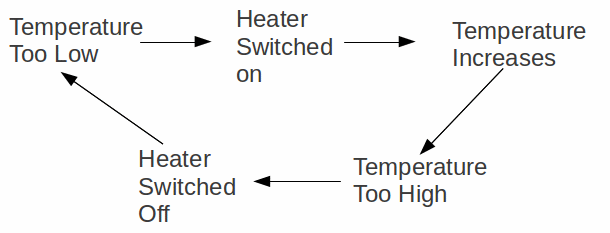
If the temperature of this room were to suddenly drop 10 degrees, what would your internal temperature be? And Why?

Homeostasis— Stable internal conditions are maintained through automatic responses and through behavior.
Our body uses a negative feedback which causes the system to return to its original state.
In 5 words or less, what does evolution mean?

– The genetic makeup of a population of a species changes.
– Evolution can occur through natural selection of adaptations.
– Adaptations are beneficial inherited traits that are passed to future generations.
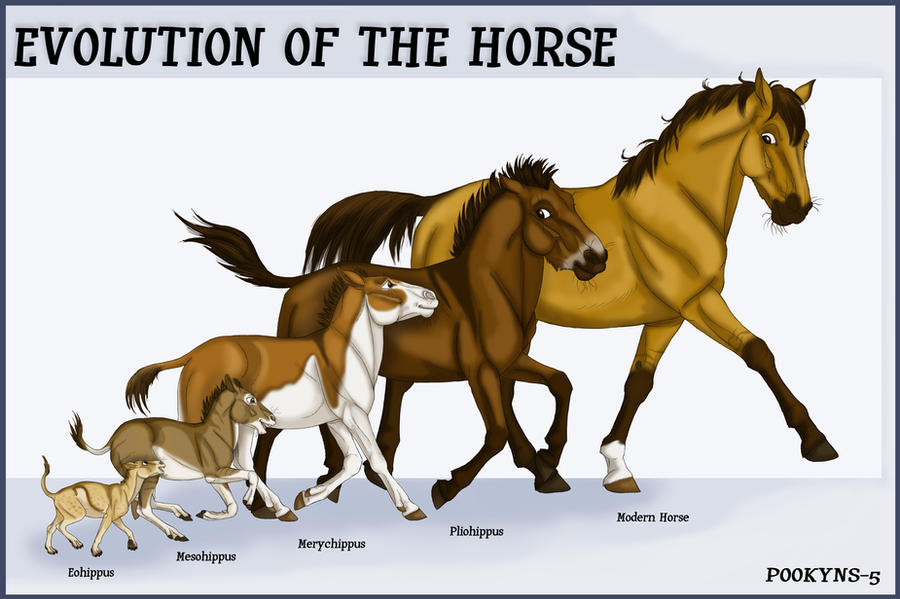
Evolution— Gradual change in genetic makeup of a population of a species.
1.2 Take home Quiz CLICK HERE
If you missed today's class here are some quick notes....
The unifying themes of biology:
- Systems—Related parts interact to form a whole. Examples include cells that work together to perform a function; different organs that work together; different organisms that interact in an ecosystem.
- Structure and Function— Function is related to structure. Examples include cell structure and function; anatomical structure and function.
- Homeostasis— Stable internal conditions are maintained through automatic responses and through behavior. Examples include temperature regulation
- Evolution— Gradual change in genetic makeup of a population of a species. Examples include adaptations in different environments resulting in different species.













Ready for the test
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDelete